On Tuesday, April 16, 2019, Attorney General William Barr released an immigration decision applying to migrants who have established "a credible fear of persecution or torture" in their home country. The decision orders immigration judges to prevent migrant asylum seekers from posting bond while awaiting trial. President Donald Trump has criticized the former immigration policy allowing the posting of bond as a "catch and release" system. The American Civil Liberties Union's Immigrants' Rights Project claims that "this decision will result in the unlawful jailing of thousands of people who should not be behind bars."
Five parents have filed a lawsuit in response to an emergency order issued last week by New York City Mayor Bill de Blasio's administration declaring a public health emergency and requiring all residents within certain Brooklyn zip codes to be vaccinated against measles or face a $1,000 fine. According to news reports, the action was filed in Brooklyn Supreme Court against the New York City Department of Health, and alleges that the order exceeds the powers of the Public Health Commissioner. It also claims that the City's measures are too drastic in light of its reasons for issuing the order. A judge denied the parents' request for an emergency injunction yesterday, but the parties will appear in court on Thursday.
The California Air Resources Board (CARB) has sued two US federal agencies over the data they used to support rolling back Obama-era vehicle emissions standards.
A New York tenant achieved an early victory in a lawsuit against his landlord based on harassment by a neighbor. This case should encourage landlords in New York and surrounding states to respond proactively to accusations of discrimination or harassment involving their tenants.
On April 2, the US House Ways and Means Committee passed H.R.1957, the Taxpayer First Act of 2019 (the “Act”). Widely cited as a win for private online tax preparation companies such as TurboTax, opponents claim it will prohibit the IRS from creating competing free software to assist citizens in tax preparation and filing…
A family whose daughter was killed in the Ethiopian Airlines 737 MAX crash filed a lawsuit against Boeing Co and Rosemount Aerospace Inc, which makes a part of the aircraft under investigation. The parents of Samya Stumo, who was on a work trip when the crash occurred on March 10 shortly after takeoff from Addis Ababa, filed the complaint in U.S. federal court in Chicago. The crash killed all 157 people on board.
The attorneys general of several states—New York, California, Illinois, Minnesota, New Mexico, and Vermont—and the District of Columbia have filed a lawsuit against the Trump administration over its weakening of the federal nutrition standards for school meals. The complaint, filed in the US District Court for the Southern District of New York, alleges that in 2018 the US Department of Agriculture weakened the federal nutritional standards for sodium and whole grains without first providing the public an opportunity to comment on them, in violation of Administrative Procedure Act.
On Tuesday, April 2, 2019, the American Civil Liberties Union and the Knight First Amendment Institute at Columbia University filed a lawsuit in the United States District Court, District of Maryland, on behalf of five former federal employees challenging the constitutionality of prepublication review. Former government and intelligence agency employees must submit manuscripts and drafts for government review before publication due to a lifelong obligation to keep national security secrets for as long as the information is considered classified by the government. The lawsuit alleges violations of both the First Amendment and the Fifth Amendment.
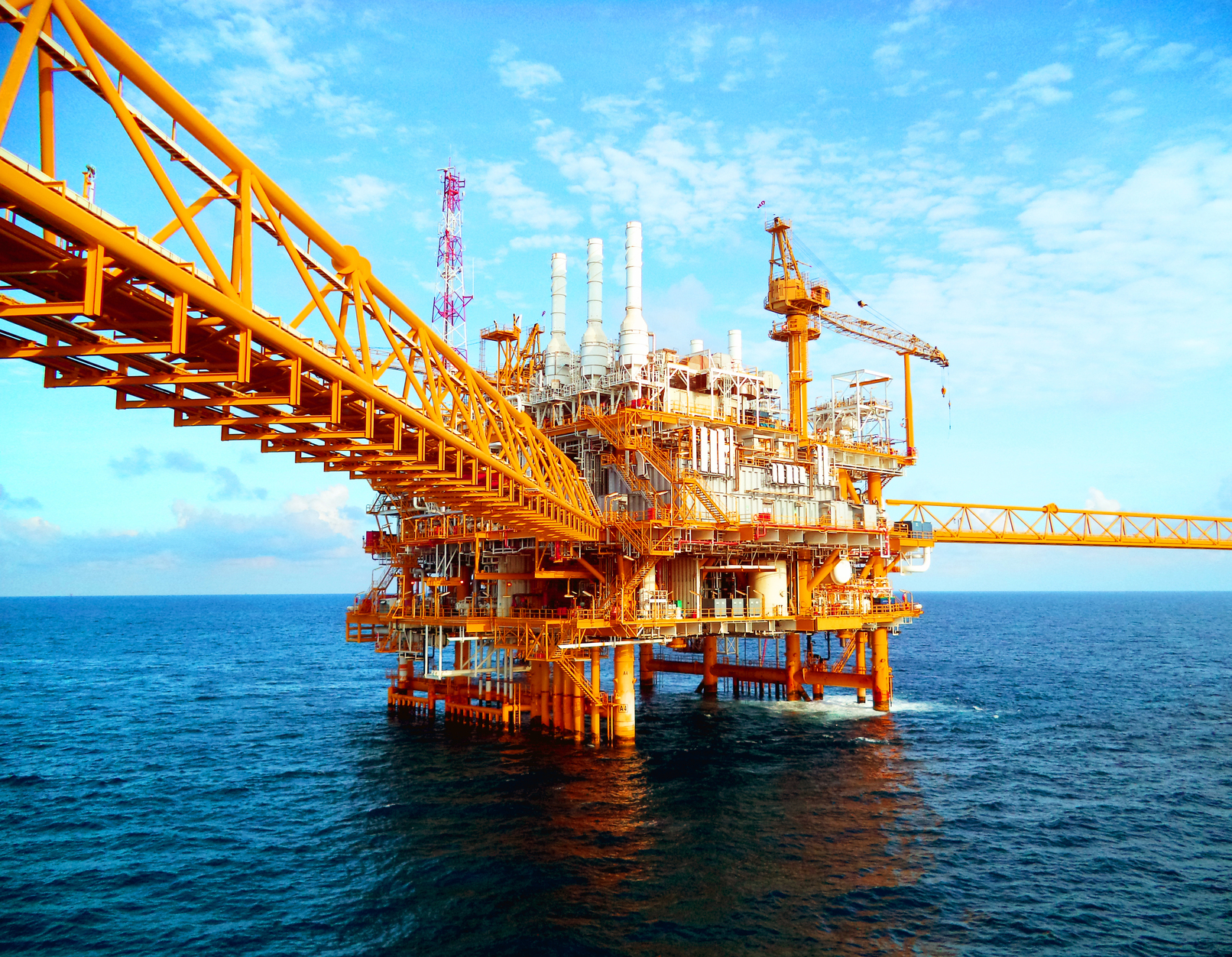
A federal judge in Alaska has ruled that President Trump does not have the authority to re-open Arctic waters to drilling that the Obama administration closed to drilling in 2016. Judge Sharon L. Gleason explained that while a 1953 law called the Outer Continental Shelf Lands Act (OCSLA) permits a president to remove waters from drilling, it does not contain a provision allowing a president to add waters to the list of available drilling sites.
Rookie justice Brett M. Kavanaugh seemed to take the place of Justice Kennedy during the arguments, suggesting that some partisan gerrymandering can be so extreme that it is unconstitutional.